In today’s fast-paced work environment, the emergence of generative AI is going to transform the way businesses operate from automating routine processes to enhancing decision-making capabilities. But how does that impact you and what do you need to know?
In this article, Karen Ko, Managing Director at Protiviti Hong Kong, explores practical applications of AI in daily work routines, highlighting how AI can simplify tasks and foster a more productive work environment as a finance professional. She explains how to write prompts, examples of use cases to get started, and tips on how to manage data when deploying AI.
How do I write a prompt?
Prompts are how you ask the AI tool to do something for you, it can be creating, summarising, editing or transforming data available. Imagine yourself having a conversation with a colleague with simple, unambiguous language such as:
- To learn about projects and concepts: “What is [Project X] and who are the key stakeholders working on it?”
- To edit content: “Compare these 2 data sets for inconsistencies.”
- To transform documents: “Transform this requirements doc into a 10-slide training guide.”
- To summarise information: “Write a session abstract of this [financial report].”
- To create engaging content: “Create a meeting invite for [Finance townhall].”
- To catch-up on missed items: “Provide a summary of the updates and action items on [Project X].”
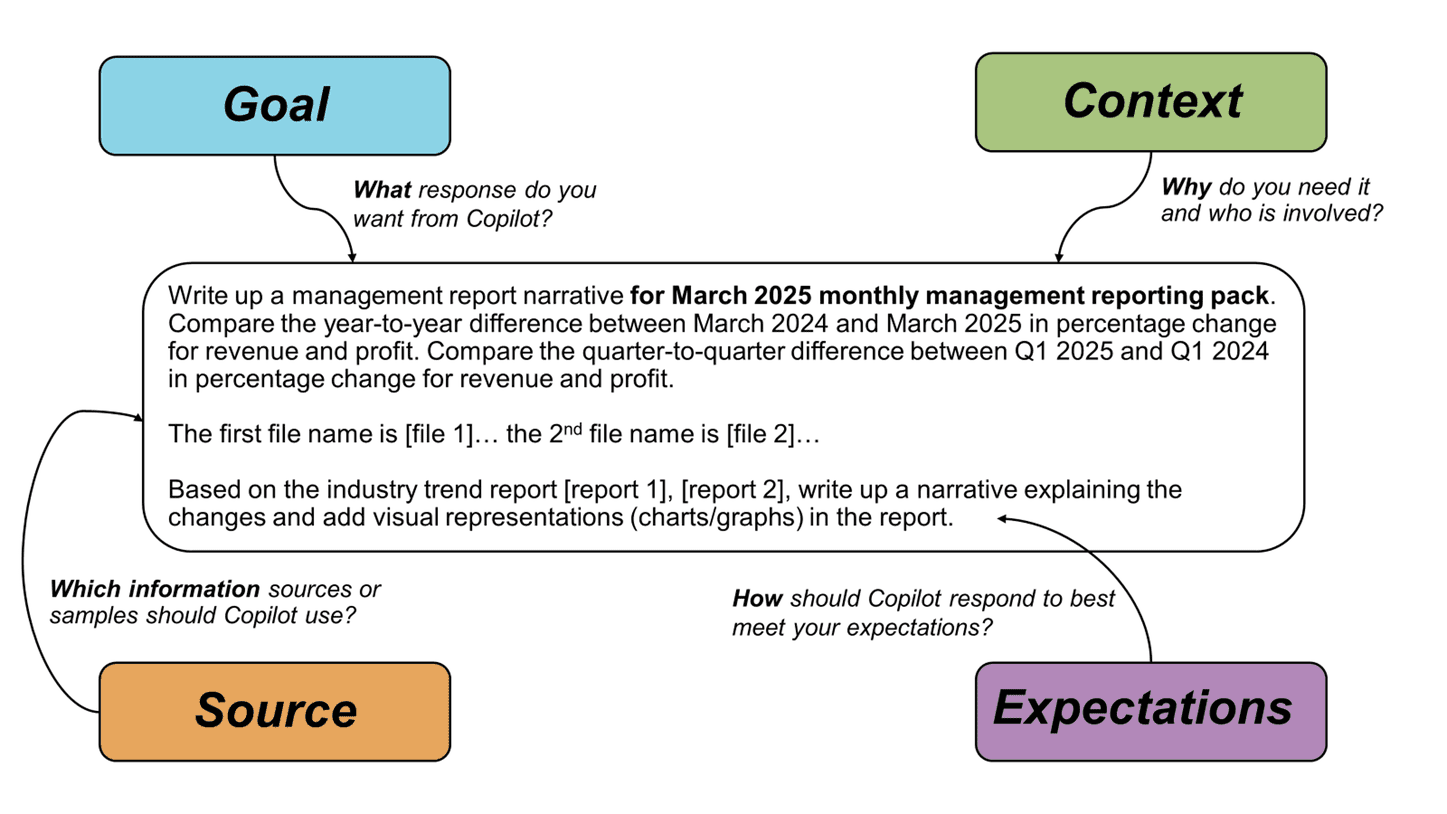
To get the best response, it is important to include four ingredients and combine them in different orders and quantities to match the desired needs:
- Goal: What do I want? What response do I want from Copilot?
- Context: Why do I need it? Who is involved?
- Source: Where to look? Which information sources should Copilot use?
- Expectations: How should Copilot respond to meet your expectations?
The following example illustrates a prompt to prepare a management report based on internal data from various datasets and external data (industry reports). The goal of this prompt is to identify changes, discrepancies, similarities, and prepare a first draft to focus the finance manager on higher value activities. Here are the details:
Whether you are looking to generate creative content, gather insights, or streamline tasks, the way you interact with AI can make all the difference. Here are some top tips to help you get the most out of your AI experience and ensure your interactions are as productive and insightful as possible.
- Tip #1: Iterate and Refine: If the first response is not right, refine your prompt and try again. For example, “Can you propose a more concise summary in 200 words of the annual report of our competitor?”
- Tip #2: Ask Follow-Up Questions: If you need more details, ask follow-up questions. For instance, “Can you describe in further details the 3rd item related to new regulatory changes?”
- Tip #3: Use Examples: If you are looking for a specific format or style, provide examples. For example, “Can you highlight all the outliers in this dataset with this font colour?”
We cover more on how to master the art of AI prompt engineering in this webinar.
AI use cases for a finance professional
AI is poised to become a helpful tool for finance department with the potential to transform daily activities in several ways:
- Conduct effective meetings: Summarise key insights and decisions from strategic planning meetings, for CFOs and stakeholders.
- Reduce time searching and gathering information: AI can also be used to summarise financial reports and news articles. This is particularly useful for finance managers who need to keep up with the latest initiatives and financial performance of their competitors.
- Improve first time drafting: Finance managers can use AI to create draft for management information leveraging the latest company-specific data and allow them to focus on strategy.
- Proof-reading: AI tools can be effective in supporting proof-reading, to check internal consistency and identify potential grammatical issues that standard built-in spellcheckers can miss.
- Financial data analysis and insight extraction: AI can assist finance manager to extract data, populate into analysis and scenarios
Some tips for managing your data when deploying AI
Data governance involves critical considerations under different regulatory environments, and the complexity and volume of financial data. Finance should also work closely with procurement, compliance, and IT team to address key risk and put in controls in place. As an example, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)’s Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework Govern 6.1 states that Policies and procedures are in place to address AI risks and benefits arising from third-party software and data and other supply chain issues. Other regulations such as the European Union AI Act, require handling personal data in compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR. It also requires professional users to be aware of incident response protocols for breaches or data leaks and know their roles and responsibilities in such events.
In addressing all the risks due to the introduction of AI tools, there are also safeguards and controls that could be put in place. For example, establish safeguards to ensure data protection (privacy, security) and data quality for AI systems/capabilities and models. Examples of safeguards include:
- Data classification assignments and reviews
- Data quality checks for data used by AI/ML systems
- Periodic reviews of production data produced by and used by AI/ML systems to identify new risks against acceptability criteria
- Validations of AI model training and test data for consistency, data quality, data protection and relevance to purpose
- Protections to guard against unauthorized access and/or inference by AI systems/capabilities to inappropriate data classifications (e.g., sensitive/restricted data)
In addressing the data copyright, Information Security Governance and Risk Management when deploying AI, which has been included in various AI guidance (NIST AI 100-1; ISO/IEC 23053:2022; EU AI act 13. Consumers, 4. Conformity), one of the safeguards could be mapping the legal and compliance risks related to AI technologies, including risk of unauthorized use of third-party intellectual property, infringement of consumer rights, and violation of privacy and data-protection laws and regulations. It is also good practice to have an Information Security Policy is in place that defines clear roles, scope, responsibilities, and objectives, as well as business strategy alignment, contractual and regulatory requirements, acceptable use of information and assets, and should contain standards related to data classification, data ownership, and data protection. Legal and Corporate Risk functions are aware of current and new AI laws and regulations. Policies, standards, and procedures for managing risks specific AI are documented and socialized across the organization.
With new risk related to data while deploying AI, we should proactively look into controls and safeguarding measures that can help us to address such risk.

