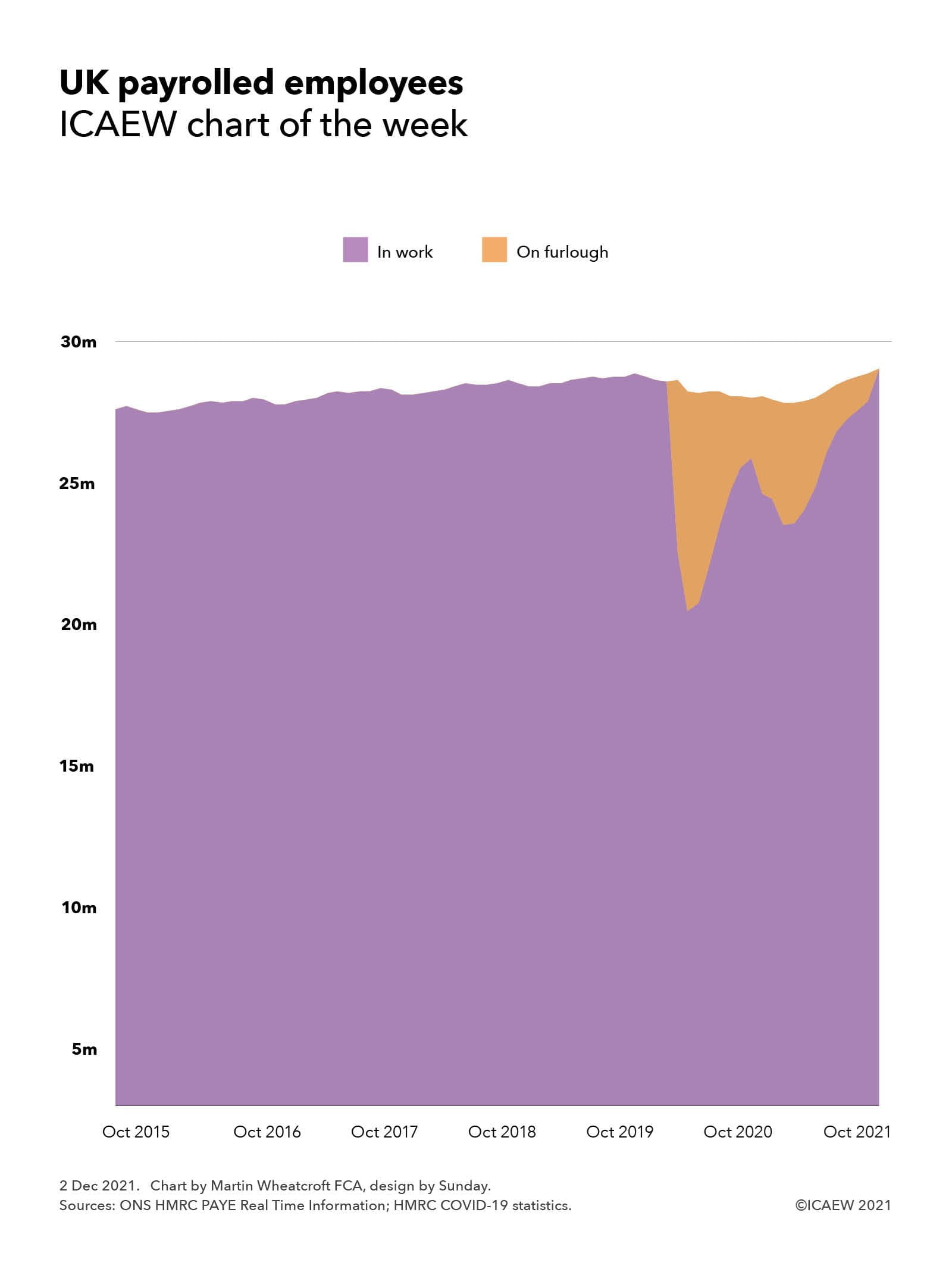
Concerns that the end of the furlough scheme in September 2021 would be followed by a sharp rise in unemployment proved to be unfounded, with the flash estimate of the number of people on UK payrolls increasing to 29.4m in October 2021, an increase of 166,000 from the previous month and greater than before the pandemic. This is positive news as it suggests that the majority of the 1.1m still on the furlough scheme when it ended on 30 September 2021 have been able to retain their jobs or have found work elsewhere.
The chart shows how payrolled employees increased gradually before the pandemic from 27.7m in October 2015 to 28.1m in October 2016, 28.5m in October 2017, 28.8m in October 2018 and 29.0m in October 2019, peaking in November 2019 at 29.1m. Numbers fell to 28.9m in February 2020 although on a seasonally adjusted basis the numbers increased slightly. Those in work fell significantly by the end of March 2020 to 22.0m when 6.8m were placed on furlough under the government’s Coronavirus Job Retention Scheme (CJRS) and to 19.7m at the end of April 2020 when 8.8m were on furlough.
Despite the furlough scheme overall payrolled numbers fell during the pandemic from 28.9m in March 2020 (including 6.8m on furlough) to 28.2m in October 2020 (when 2.4m were on furlough) to 28.0m at its lowest in January and February 2021 (when 4.9m and 4.7m were on furlough), before gradually rising to 29.2m in September 2021 (when 1.1m were on furlough) and 29.4m in October 2021 (when no one was on furlough).
Although the flash numbers for October 2021 are provisional and subject to change, they should be sufficiently reliable for policy makers to take some comfort that the furlough scheme has done its job in stabilising the economy and avoiding significant levels of unemployment. However, with the pandemic still not over, there will be concerns about whether growth in employment can be maintained over the coming months.
According to the ONS, the median monthly pay in October 2021 was £2,005, slightly down on the £2,010 reported for September 2021, but an increase of 4.9% compared with the £1,911 calculated for October 2020. The latter compares with consumer price inflation of 4.2% over the same period.
The idea that we might be emerging from the pandemic with higher levels of employment and wages than before it started might have seemed unlikely at the start of the first lockdown. But then at an estimated total cost of £370bn, of which £70bn was for the CJRS, the eye watering sums incurred by the government in getting to this position have been far from insubstantial.


