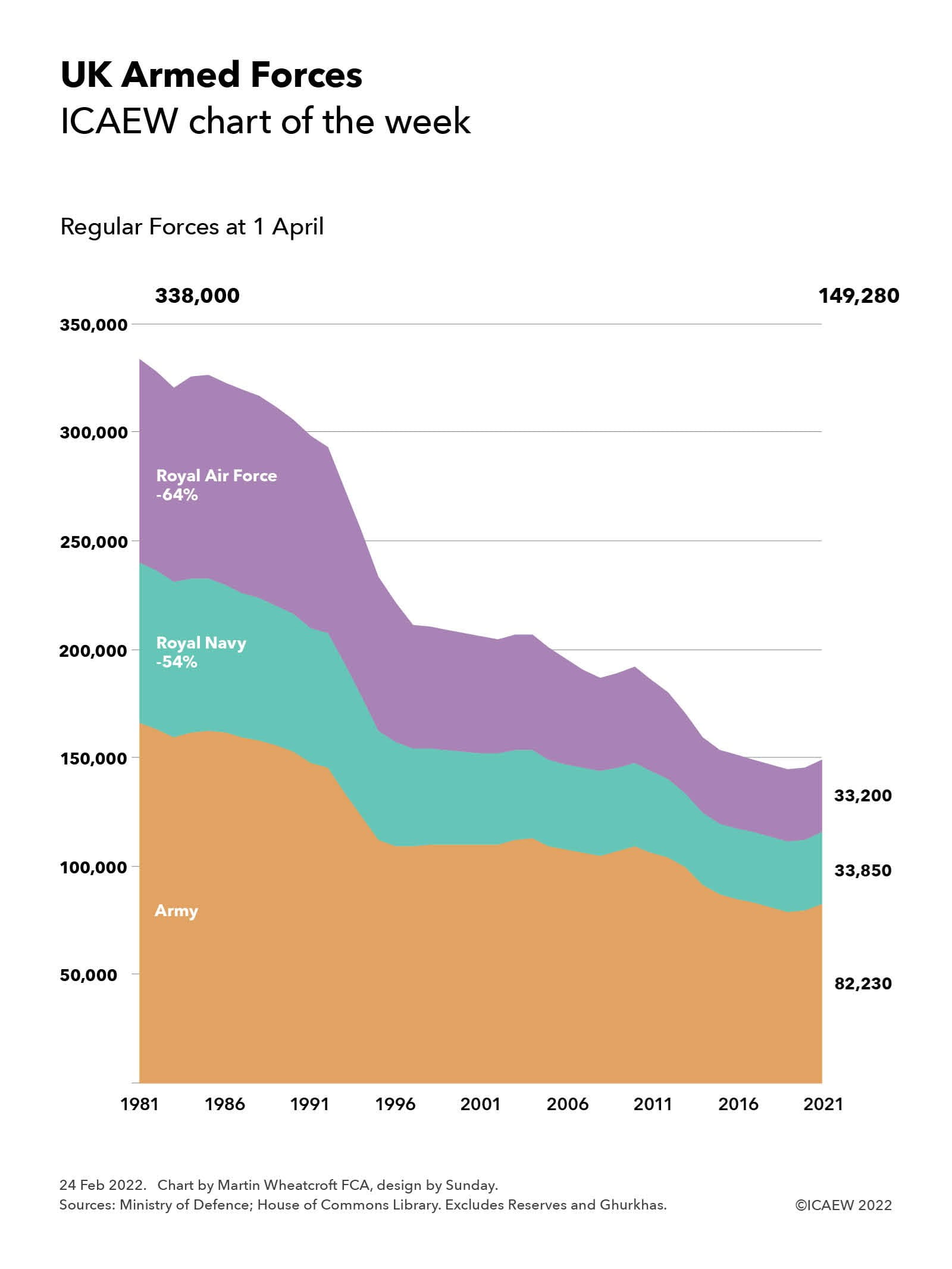
The post-Cold War ‘peace dividend’ has been reflected in a decline in defence spending over the past 40 years, accompanied by fewer soldiers, aviators, sailors and marines, as illustrated by our chart of the week. This shows how regular force numbers have fallen from 338,800 on 1 April 1981 (comprising 166,000 in the Army, 74,300 in the Royal Navy, including the Royal Marines, and 93,500 in the Royal Air Force) to 149,280 on 1 April 2021 (comprising 82,230 soldiers, 33,850 sailors and marines and 33,200 aviators).
There has been a small rise in numbers in the past couple of years as improvements to recruitment have helped bring the armed forces up to its planned complement.
The substantial falls in service personnel numbers since the 1980s have been accompanied by significant reductions in the numbers of tanks, ships and aircraft in operation – although technological and warfare developments mean that modern defence equipment is much more powerful than its predecessors. The two Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers recently commissioned by the Royal Navy are a case in point.
The numbers in the chart exclude Army, Navy and Air Reserves of 37,420, Ghurkas of 4,010 and other military personnel of 8,170, at 1 April 2021. Also not included are civilians working for the Ministry of Defence or for the security services, who are also important parts of the UK’s national defence and security capability.
Last year’s Integrated Review of Security, Defence, Development and Foreign Policy included plans for greater investment in military equipment and cyber warfare, but it also set out further reductions in regular force numbers, with the Army expected to reduce to fewer than 75,000 by 2024.
Whether these plans will be revised in the context of a war in Europe remains to be seen, but it seems likely that the government will, at the very least, need to re-evaluate its plans. This may have implications for public finances as pressure will probably grow for spending on defence to increase from the £46bn – just under 2% of GDP – budgeted in the current financial year.
However, as the pandemic has perhaps demonstrated, the costs of being inadequately prepared for future eventualities – both in lives and money – could end up being significantly greater in the long run.


