Hello all and welcome back to the Excel Tip of the Week. This week we are concluding our three-part series examining different methods for building an audit sampling template with a Developer level post, working on solving the problem with VBA code.
You can compare and contrast this method with the new dynamic arrays or with traditional Excel formulas.
This post’s subject was also covered as the closing part of our EuSpRIG 2020 talk, which you can see on YouTube:
The key differences
Just like our previous two examples, we are going to be working with a standard 100-item set of transactions to sample. In the first two parts of this series, we looked at how to solve this problem with two different kinds of formulas. This time, we are using VBA macros – and that means that most of the inputs are not on the face of the workbook, but instead form part of our macros. Our screen now looks like this:
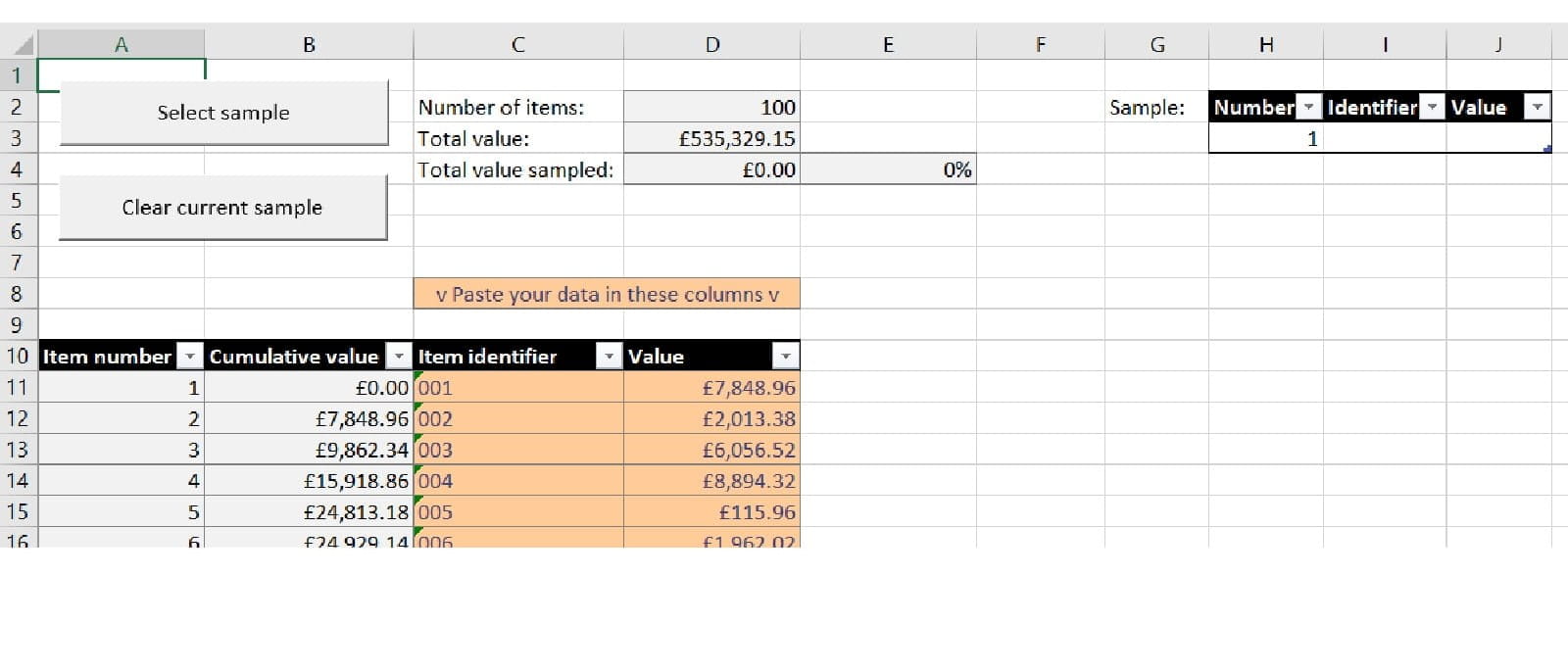
In terms of advantages and disadvantages, the VBA alternative is probably the easiest to use, but it’s also the hardest to update or fix if anything goes wrong – VBA coding is much less understood and harder to review than formulas. It also requires that we use a .xlsm file – which for security reasons not all systems allow.
Let’s see how this works in practice.
Getting started
Our ‘Select sample’ button runs this macro:
Sub Start()
Dim Sampling As String
Sampling = InputBox("Enter 1 for Unit sampling or 2 for Monetary unit sampling.")
If Sampling = 1 Then
Call UnitSampling
Else
If Sampling = 2 Then
Call MonetarySampling
Else
MsgBox ("You must enter a value of either 1 or 2.")
Call Start
End If
End If
End Sub
This is a pretty straightforward macro – it asks the user to indicate which kind of sampling they want, and then runs the appropriate sub according to their selection. We include an Else that prompts the user if they try entering some other value to add some robustness.
We’ll start by building up the code for our UnitSampling sub – which as a reminder will just pick n items at random from the list. We’ll start with the basic framework:
Sub UnitSampling()
Dim SampleSize As Integer
SampleSize = InputBox("Enter your desired sample size:")
If SampleSize > Range("Sampling").Rows.Count Then
MsgBox ("Sample size cannot exceed the number of items in the sample.")
Exit Sub
Else
End If
Dim SampleArray As New Collection
Dim NewCandidate As Integer
Dim Repeat As Boolean
[code to pick our sample]
[code to output the sample]
End Sub
We start with another InputBox which we use to get the desired sample size from the user. We once again have a logic check in place – this time to prevent the user choosing a number larger than the total population size, which would cause an infinite loop later on. Then we set up some variables which we will be using as we identify our items later on. The most significant type we’re using here is a Collection – see TOTW #260 for more on those.
Now for our first loop, in which we’ll pick the required number of distinct items from our range. To do this we will generate random numbers and then check them against what we’ve already picked to make sure we aren’t getting duplicates. We keep doing this until we have the required number of items, so we’re using a Do While statement. Here’s the code:
Do While SampleArray.Count < SampleSize
Repeat = False
NewCandidate = WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(1, Range("Sampling").Rows.Count)
If SampleArray.Count = 0 Then
Else
For j = 1 To SampleArray.Count
If SampleArray(j) = NewCandidate Then
Repeat = True
Else
End If
Next j
End If
If Repeat Then
Else
SampleArray.Add (NewCandidate)
End If
Loop
We use the Repeat flag to identify whether our current random number has already been used or not. We then generate a random row number from the table, check whether or not that random number is already in our sample. And if not we add it.
Finally we need a simple loop to output our random sample:
For i = 1 To SampleArray.Count
Range("Picked[[#Headers],[Identifier]]").Offset(i, 0) = WorksheetFunction.Index(Range("Sampling[Item identifier]"), SampleArray(i))
Range("Picked[[#Headers],[Identifier]]").Offset(i, 1) = WorksheetFunction.Index(Range("Sampling[Value]"), SampleArray(i))
Next i
This just loops through the SampleArray collection and then populates our output Table – called Picked – with the results.
Monetary unit sampling
This starts out much the same way as before:
Sub MonetarySampling()
Dim SampleSize As Integer
SampleSize = InputBox("Enter your desired sample size:")
If SampleSize > Range("Sampling").Rows.Count Then
MsgBox ("Sample size cannot exceed the number of items in the sample.")
Exit Sub
Else
End If
Dim SampleArray As New Collection
Dim NewCandidate As Long
Dim Repeat As Boolean
Dim MonetarySize As Long
MonetarySize = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("Sampling[Value]")), 0)
[code to pick the sample]
[code to output the sample]
End Sub
We have one additional variable here, which is MonetarySize – we use this to identify the total value of the items being sampled, as we will be using this value frequently, so storing the value in a variable will be easier.
The core loop we use to pick our sample is essentially the same as before, only with an extra step: To avoid duplicates, we can’t just pick N different monetary units, but instead have to map each candidate onto the sample item it represents, and then check that mapped item against the list. This adds a few extra steps:
Do While SampleArray.Count < SampleSize
Repeat = False
NewCandidate = WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(1, MonetarySize)
NewCandidate = WorksheetFunction.Index(Range("Sampling[Item number]"), WorksheetFunction.Match(NewCandidate, Range("Sampling[Cumulative value]"), 1))
If SampleArray.Count = 0 Then
Else
For j = 1 To SampleArray.Count
If SampleArray(j) = NewCandidate Then
Repeat = True
Else
End If
Next j
End If
If Repeat Then
Else
SampleArray.Add (NewCandidate)
End If
Loop
The output code is the same as before.
Wrapping up
In the full EuSpRIG 2020 talk which we linked above, we make some important points about comparing and contrasting these three approaches to solving the same problem. There’s no “right” answer here – each has its own strengths and weaknesses. That’s often – perhaps even always – the way that Excel problems fall out. Depending on your circumstances, the right answer can change – so always keep that in mind!
You can download the file and read over the full code for yourself here.
Archive and Knowledge Base
This archive of Excel Community content from the ION platform will allow you to read the content of the articles but the functionality on the pages is limited. The ION search box, tags and navigation buttons on the archived pages will not work. Pages will load more slowly than a live website. You may be able to follow links to other articles but if this does not work, please return to the archive search. You can also search our Knowledge Base for access to all articles, new and archived, organised by topic.

