Sometimes, you want find the position of the nth item in a list rather than the first necessarily. For example, you might wish to locate the seventh item on an invoice or the third sibling in a family to attend school, etc. Presently, Excel has no standard function for this although the first match can be found easily using the MATCH function:
MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_list, [match_type])
which returns the relative position of the first item in a list that (approximately) matches a specified value. However, this is neither case sensitive nor allows for selecting later occurrences.
To demonstrate a suggested solution, let’s consider the following example:
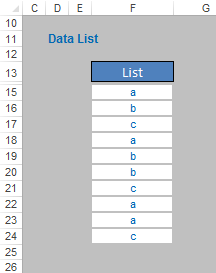
Imagine we wished to locate the position in the list of the third occurrence of the letter “a”. This occurs in row 22, which happens to be the eighth item in the list, i.e. the position is eight [8].
This calls for an “old school” array formula (if you don’t have Excel 365):
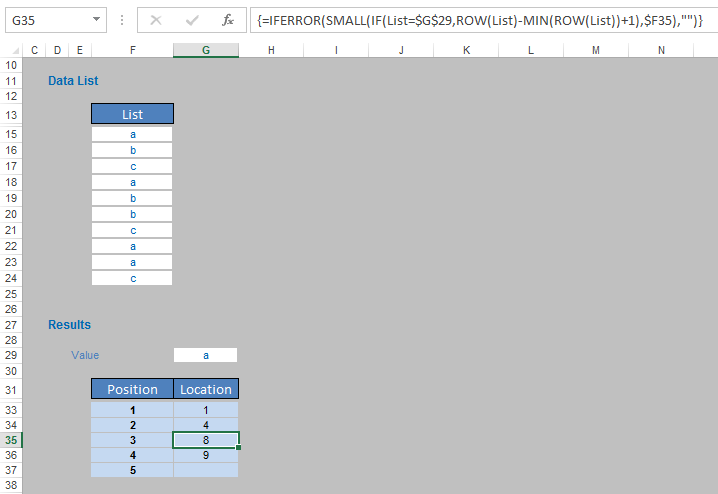
{=IFERROR(SMALL(IF(List=”a”,ROW(List)-MIN(ROW(List))+1),n),"")}
You only need to press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER if you are using older versions of Excel, as array formulae no longer need these braces (you can’t just type them in). This is an array formula as calculations are being considered across multiple cells (IF(List=”a”,…). In this case, List would be the column vector F15:F24 and n would be three [3], viz.
Essentially, array formulae perform multiple calculations on one or more of the items in an array and are entered using CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER (the braces, “{“ and “}” then appear, they cannot be typed in). Array formulae can return either multiple outputs or a single result. There are two types:
- Formulae that work with an array or series of data and aggregate it, typically using SUM(), AVERAGE(), MIN(), MAX() or COUNT(), to return a single value to a single cell. Microsoft calls these single cell array formulae.
- Formulae that return a result in to two or more cells (there are various formulae that will do this including MINVERSE(), LINEST() and TRANSPOSE()). These types of array formulas return an array of values as their result, and are referred to as multi-cell array formulae.
The solution here is an example of a single cell array formula. It returns a single value after aggregating a range of data.
To understand how this formula works, let’s look at the formula from inside to out, starting with ROW(List)-MIN(ROW(List))+1. The ROW function takes the row number so ROW(List)-MIN(ROW(List))+1 calculates the position of an element in List relative to the first item in the list (e.g. if the list started on row 1, then the second item on the list would be ROW(Row 2)-MIN(ROW(i.e. Row 1))+1) which would be 2-1+1 which equals 2.
IF(List=”a”,ROW(List)-MIN(ROW(List))+1) produces an array of positions which contain the letter “a”, i.e. {1,4,8,9} in our example list. It should be noted that it is commonplace in array IF formulae not to specify what should happen if the condition is false (it is assumed the value is FALSE or zero).
The SMALL(List,n) function finds the nth smallest value in a list. Therefore, in our formula SMALL(IF(List=”a”,ROW(List)-MIN(ROW(List))+1),n) this finds the nth smallest item, so the third smallest value of {1,4,8,9} is 8.
Finally, IFERROR(SMALL(IF(List=”a”,ROW(List)-MIN(ROW(List))+1),n),"") uses IFERROR to return “” (i.e. an empty cell) if we are looking for the nth item in the list where n is larger than the number of items in the list. This stops #NUM! being returned as a value and makes the formula ‘tidier’.
Since the formula considers a range of cells, this needs to be entered as an array formula – hence the braces.
Word to the wise
If you want to find the nth value from the bottom up (instead of from the top down), use the LARGE function instead of the SMALL function.
Excel community
This article is brought to you by the Excel Community where you can find additional extended articles and webinar recordings on a variety of Excel related topics. In addition to live training events, Excel Community members have access to a full suite of online training modules from Excel with Business.

Archive and Knowledge Base
This archive of Excel Community content from the ION platform will allow you to read the content of the articles but the functionality on the pages is limited. The ION search box, tags and navigation buttons on the archived pages will not work. Pages will load more slowly than a live website. You may be able to follow links to other articles but if this does not work, please return to the archive search. You can also search our Knowledge Base for access to all articles, new and archived, organised by topic.
